Windows Search Multi-User – Outlook Search Issues
The issue encountered concerns abnormal behavior of Windows Search within Outlook on a Hyper-V virtual machine where multiple users connect remotely at the same time. The problem became more pronounced after upgrading to Windows 11.
Thinstuff XP/VS Terminal Server is installed to enable simultaneous multi-user access.
The issue presents two recurring anomalies:
-
Searches within Outlook return no results, or
-
Searches return partial results and are extremely slow.
The indexing process is very slow and appears never to complete.
Standard Procedures for Windows Search Issues
The usual procedures adopted to restore correct search functionality are the following, as reported on the Microsoft website and reproduced here in full: Microsoft website
Solution 1: Restart the Windows Font Cache Service
In some cases, Windows Search issues can be resolved by restarting the Windows Font Cache Service. To do so, follow these steps:
-
In the search box on the taskbar, type services.msc to open the Services console.
-
In the right pane, right-click Windows Font Cache Service and select Stop.
-
Try performing the search again.
-
In the Services console, right-click Windows Font Cache Service and select Start.
Solution 2: Check for Updates
When using Windows 11 or Windows 10, you can choose when and how to receive the latest updates to keep your device running smoothly and securely.
To manage update options and view available updates:
-
Select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates.
Install any available updates and restart the computer if required.
For more information, see Update Windows.
Solution 3: Run the Search and Indexing Troubleshooter
Windows automatically indexes content to provide faster search results. If you are using Windows 10 version 1903 (May 2019 Update) or later, and Windows detects a problem, it automatically runs the search troubleshooter, which resets Windows Search to its default settings.
To view the troubleshooter history:
-
Select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > View troubleshooting history.
To manually run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter:
-
Open a Command Prompt window and run the following command:
-
Run the troubleshooter and select any applicable issues.
Windows will attempt to detect and fix them.
For more information on search and indexing, see:
-
Performance issues affecting Windows Search
-
Windows 10 Search Indexing: Frequently Asked Questions
Solution 4: Restart Windows Search
Follow these steps to end the SearchUI.exe (Windows 10) or SearchHost.exe (Windows 11) process. Stopping this process stops Windows Search. The next time you perform a search, Windows Search will restart automatically.
-
Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, then select Task Manager.
-
In Task Manager, select Details.
-
In the Name column, right-click SearchUI.exe or SearchHost.exe, then select End task.
-
When prompted, select End process.
If this does not resolve the issue, try restarting the device. Restarting also installs any pending updates.
Note:
Before restarting, consider bookmarking the relevant support page.
Solution 5: Reset Windows Search
Try resetting Windows Search using the procedure appropriate for your Windows version.
To determine the Windows version:
-
Select Start > Settings > System > About.
Note:
Resetting Windows Search does not affect your files, but it may temporarily affect the relevance of search results.
Reset Windows Search on Windows 10 version 1809 or earlier
If the computer is running Windows 10 October 2018 Update or earlier:
-
Select Start, right-click Cortana, then select More > App settings.
-
In Cortana settings, select Reset.
Reset Windows Search on Windows 11 or Windows 10 version 1903 or later
If the computer is running Windows 11, Windows 10 May 2019 Update, or later, you can use a Windows PowerShell script.
Important:
Administrator privileges are required to run this script.
If script execution is disabled by organizational policy, contact your administrator.
Steps:
-
Check the PowerShell execution policy by opening an elevated PowerShell window and running:
-
If the policy is Unrestricted, proceed to the next step.
Otherwise, note the current value and run:
Confirm the warning by selecting Y and pressing Enter.
-
Close the PowerShell window.
-
Download ResetWindowsSearchBox.ps1 from the Reset Windows Search PowerShell script page and save it locally.
-
Right-click the file and select Run with PowerShell.
-
When prompted, select Yes to allow the app to make changes.
The script resets Windows Search.
When the word Done appears:
-
If no execution policy changes were made, close PowerShell.
-
If changes were made, restore the previous execution policy:
Replace <PreviousValue> with the original value returned by Get-ExecutionPolicy.
Close PowerShell.
Note:
If the execution policy is incorrect, an error such as “Cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system” may appear. Repeat the steps above and rerun the script.
Solution 6: Rebuild the Microsoft.Windows.Search AppData Folder
Note:
Use the Windows Recovery Environment or sign out and log in with another user account.
Important:
This procedure involves modifying the Windows Registry. Incorrect changes can cause serious issues. Back up the registry before proceeding.
Steps:
-
Verify that Windows Search works for a newly created Windows account.
-
Delete the following folder:
-
Windows 10:
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Packages\Microsoft.Windows.Search_cw5n1h2txyewy -
Windows 11:
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Packages\MicrosoftWindows.Client.CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy
(In older versions, the folder may be named Microsoft.Windows.Cortana_cw5n1h2txyewy.)
-
-
Log in with the affected account and open Registry Editor.
-
Navigate to:
-
Delete the Search registry key.
-
Open an elevated PowerShell window and run:
Windows 10:
Windows 11:
-
Restart the computer.
This restarts search indexing and regenerates both the registry key and the AppData folder.
Outlook Specific Fix:
Since the previous procedures did not resolve the issue, the following Microsoft-recommended fix was applied: Microsoft website
- Log in to the affected PC or VM as a local administrator.
- Select Start and type Registry Editor.
- Open Registry Editor.
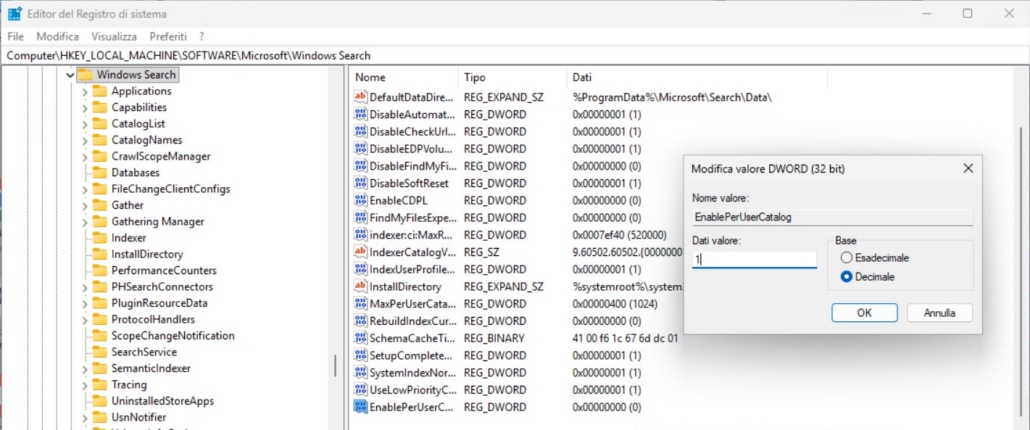
- Enable per-user Windows Search catalogs
-
- Navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search
- Create a DWORD (32 bit) value named: EnablePerUserCatalog and set its decimal value to 1
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search: "EnablePerUserCatalog"=dword:00000001
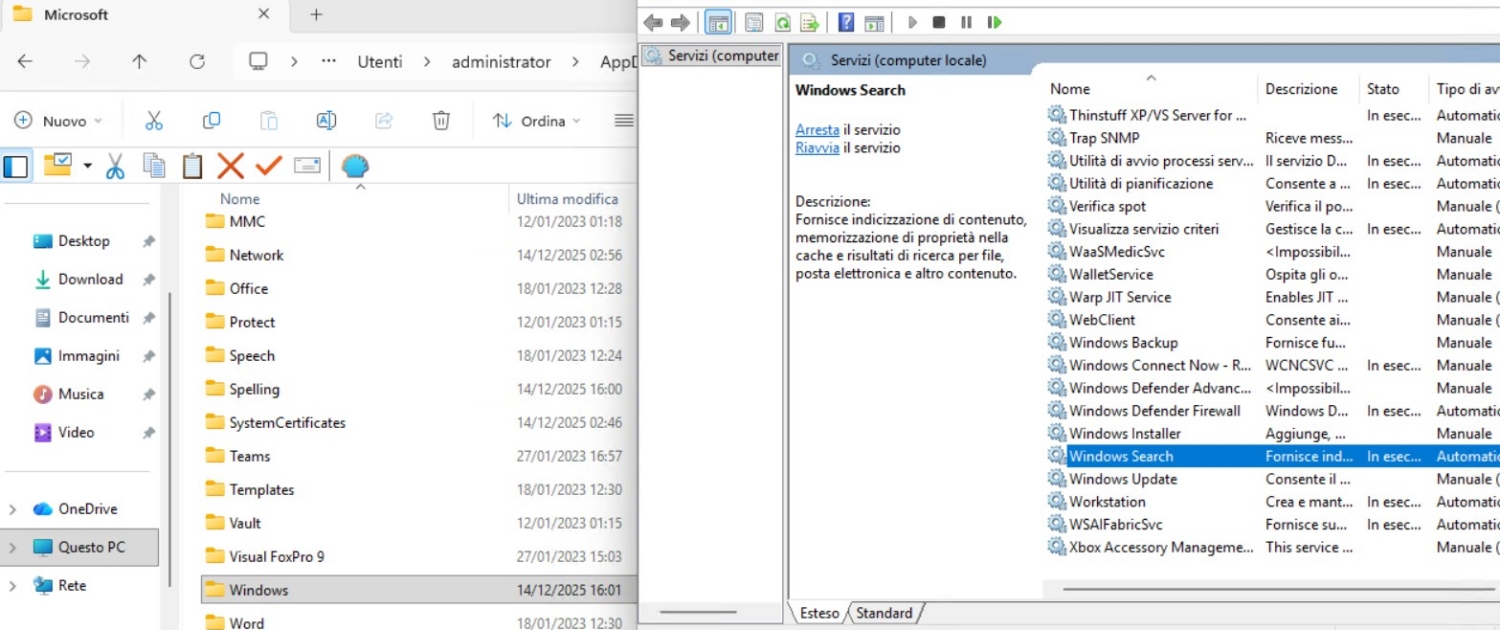
Restart the Windows Search service.
Folders named Search will be generated for each user profile under:
C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft .
Start situation:
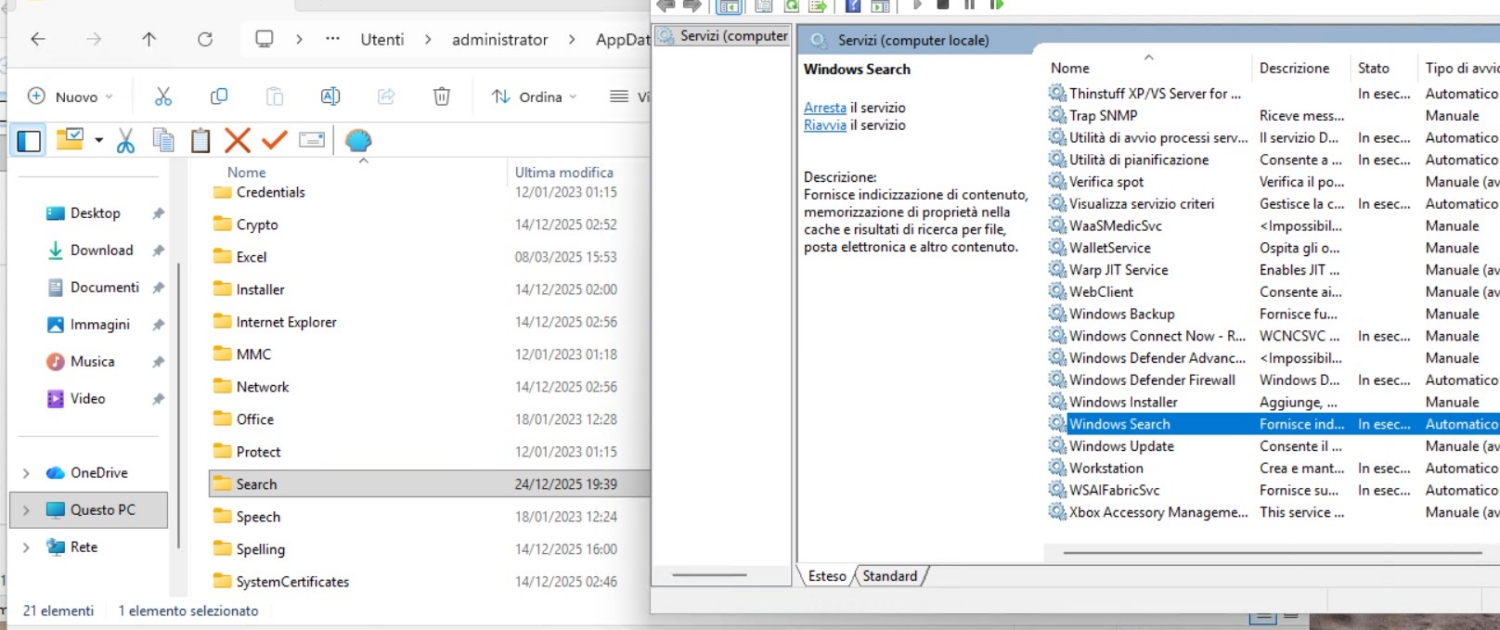
After fix situation:
Additional Remedial Steps: Rebuild Index and Run SCANPST
In some cases, it was also necessary to rebuild the Windows Search index.
In other cases, the issue affected only specific users, requiring the use of the SCANPST tool to repair Outlook data files.
The path to the Microsoft Outlook Inbox Repair Tool is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16 (for Office 2016 and later versions)
Notes on Office Versions
From a software architecture perspective, Microsoft has retained the internal version number 16.0 for all “perpetual” Office versions released over the last ten years.
Office versions and builds as of 2025:
-
Office 2016: Internal version 16.0 (support ends October 14, 2025)
-
Office 2019: Internal version 16.0 (shares binaries with Office 2016)
-
Office 2021: Internal version 16.0
-
Office 2024: Internal version 16.0 (released late 2024, latest LTSC/perpetual version)